Ie at constant pressure V T or VT constant. Atm p absolute For example a car tire pumped up to 25 atm 3675 psig above local atmospheric pressure let say 1 atm or 147 psia locally will have an absolute pressure of 25 1 35 atm 3675 147 5145.

Gauge Pressure Absolute Pressure And Pressure Measurement Physics
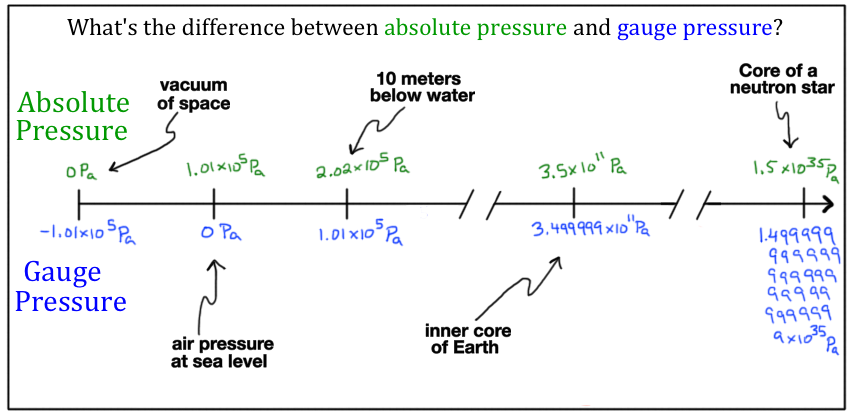
What Is Pressure Article Fluids Khan Academy

Absolute And Gauge Pressure Difference Cheaper Than Retail Price Buy Clothing Accessories And Lifestyle Products For Women Men
An absolute contraindication is a situation which makes a particular treatment or procedure absolutely inadvisable.

Absolute pressure definition. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface areaMany techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuumInstruments used to measure and display pressure in an integral unit are called pressure meters or pressure gauges or vacuum gauges. Seawater Properties - Seawater - density saturation pressure specific heat electrical conductivity and absolute viscosity. At sea level it is.
It also gives the correct answer for absolute pressure assuming you are measuring psia which is the pressure relative to absolute zero vacuum. Absolute zero temperature at which a thermodynamic system has the lowest energy. Absolute ăbsə-loot ăbsə-loot adj.
The real number of white blood cells WBCs that are neutrophils. P vacuum p absolute. It simply means there is no pressure in excess of the local atmospheric pressure.
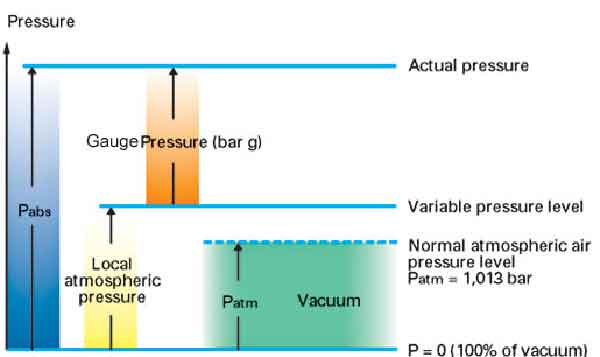
The vacuum pressure is articulated as Vacuum Pressure Atmospheric Pressure Absolute Pressure. An absolute pressure of zero corresponds to empty space or a complete vacuum. P abs P atm P gauge.
Definition of gauge pressure. Absolute pressure is a pressure that is relative to the zero pressure in the empty air-free space of the universe. However upper-case P is widely used.
Viscosity - Absolute Dynamic and Kinematic - Vicosity is a fluids resistance to flow and can be valued as dynamic absolute or kinematic. Temperature synonyms temperature pronunciation temperature translation English dictionary definition of temperature. The difference between the stagnation pressure and the static pressure measured with a Pitot tube in case of air is 412 lbfft2 where static pressure is 145 psi absolute and air temperature is 60.
Not limited by restrictions or exceptions. The IUPAC recommendation for pressure is a lower-case p. According to the ideal gas law when a gas is compressed into a smaller volume.
Steam Viscosity - Absolute viscosity of steam at pressure ranging 1 - 10000 psia. Absolute pressure is measured with reference to an absolute and theoretical vacuum. The coldest theoretical temperature is called absolute zeroIt is the temperature where the thermal motion of particles is at its minimum not the same as motionless.
Charles Law or Law of Volume states that at constant pressure the volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. It was noted that gases seem to contract indefinitely as temperature. In children for example aspirin is almost always contraindicated because of the danger that aspirin will cause Reye syndrome.
Pressure measurement is the analysis of an applied force by a fluid liquid or gas on a surface. For instance an absolute pressure of 80 kPa may be described as a gauge pressure of 21 kPa ie 21 kPa below an atmospheric pressure of 101 kPa. Temperature is the property of matter which reflects the quantity of energy of motion of the component particles.
P vacuum p absolute. It is a comparative measure of how hot or cold a material is. Absolute zero -.
The force applied is perpendicular to the surface of objects per unit area. The notion that there is an ultimately lowest temperature was suggested by the behaviour of gases at low pressures. T is the absolute temperature and C1.
Unit of pressure is Pascals Pa. For example an ordinary pressure gauge reading of zero does not mean there is no pressure. Also called detection thresholdWhat is the finest line the human eye can see the faintest sound the ear can hear the slightest taste the tongue can detect.
Note the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry IUPAC applies a more stringent standard of STP as a temperature of 27315 K 0 C 32 F and an absolute pressure of exactly 100000 Pa 1 bar 145 psi 098692 atm. Osmotic pressure is defined as the hydrostatic pressure required to stop the flow of water and thus osmotic and hydrostatic pressures are. Osmotic Pressure Definition.
It is denoted with the subscript abs. Cn are the molar concentrations of all solutes ions and molecules. Where p gauge is the gauge pressure.
This reference pressure is the ideal or absolute vacuum. The basic formula for pressure is FA Force per unit area. Similarly the osmotic pressure across of membrane separating two solutions is.
The conversion factor that needs to be used to convert between gauge pressure and. Osmotic pressure can be thought of as the pressure that would be required to stop water from diffusing through a barrier by osmosisIn other words it refers to how hard the water would push to get through the barrier in order to diffuse to the other side. Pressure is the amount of force applied at right angles to the surface of an object per unit area.
Absolute definition free from imperfection. STP Definition in Chemistry. Now as c 2 T thus at a constant pressure for a given mass of a gas V T.
The ANC is not measured directly. Unconstrained by constitutional or other provisions. The usage of P vs p depends upon the field in which one is working on the nearby presence of other symbols for quantities such as power and momentum and on.
P atm is atmospheric pressure. Absolute neutrophil count. This is a change from their earlier standard changed in 1982.
Atm p absolute For example a car tire pumped up to 25 atm 3675 psig above local atmospheric pressure let say 1 atm or 147 psia locally will have an absolute pressure of 25 1 35 atm 3675 147 5145. It corresponds to 27315 C on the Celsius temperature scale and to 45967 F on the Fahrenheit temperature scale. The absolute neutrophil count is commonly called the ANC.
An absolute threshold is the smallest level of stimulus that can be detected usually defined as at least half the time. The above form works if you are measuring differential pressure such as the difference in psi between two points. The gauge pressure is defined as the difference between an absolute pressure P abs and the.
It is derived by multiplying the WBC count times the percent of neutrophils in the differential WBC count. Unqualified in extent or degree. The symbol for it is p or P.
Absolute pressure of a gas or liquid is the total pressure it exerts including the effect of atmospheric pressure. Absolute pressure formula p abs is given by. He relied on somesthesia to warn him of pressure changes.
The minimum level of stimulation that can be detected 50 per cent of the time. The term is often used in neuroscience and experimental research and can be applied to any stimulus that can be detected by the human senses including sound touch. Pressure is defined as the physical force exerted on an object.
For instance an absolute pressure of 80 kPa may be described as a gauge pressure of 21 kPa ie 21 kPa below an atmospheric pressure of 101 kPa. Types of Pressures are Absolute Atmospheric Differential and.

What S The Difference Between Gauge Absolute Vacuum And Atmospheric Pressure Mechanical Engineering Concepts And Principles

Difference Between Bar And Barg Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
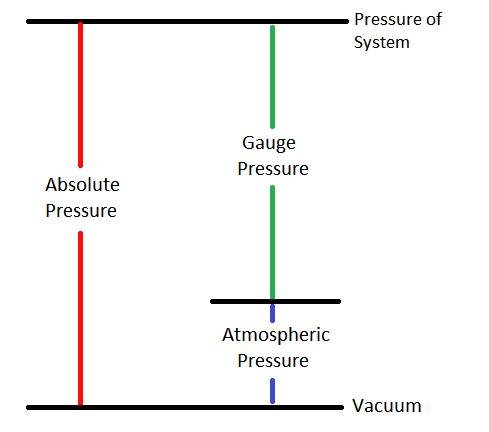
Absolute Pressure Energy Education

Difference Between Gauge And Absolute Pressure Measurement
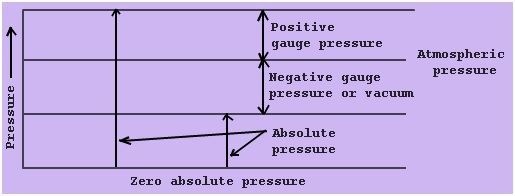
Absolute Pressure Definition Physics Meaning Of Absolute Pressure
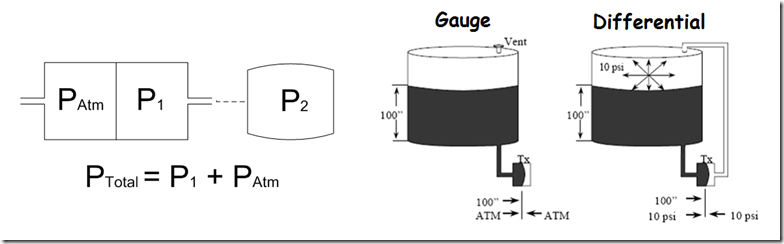
What Is The Difference Between Absolute Gauge And Differential Pressure
Absolute Pressure

Definition Of Gauge Pressure And Absolute Pressure In Hindi Formula And Example Dear Hindi Meaning In Hindi
